Boolean Pro¶
Boolean Pro is designed to act as a replacement for Blender's built-in boolean modifier, and provides extra functionality. For reference, documentation for Blender's built-in modifier can be found here.
Add-on
The normalMagic Add-on includes operators to quickly set up the Boolean Pro modifier, similar to the Bool Tool add-on.
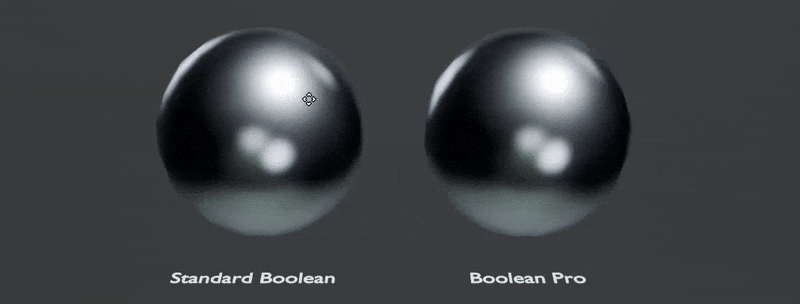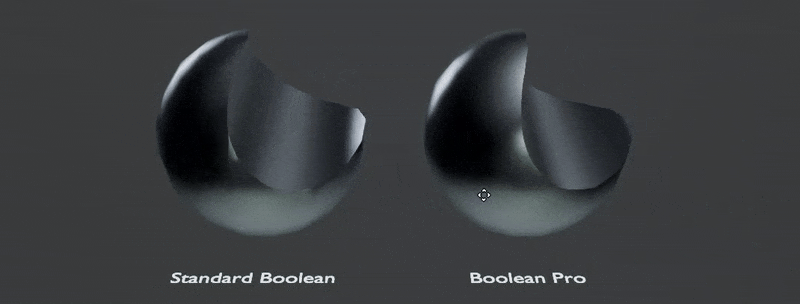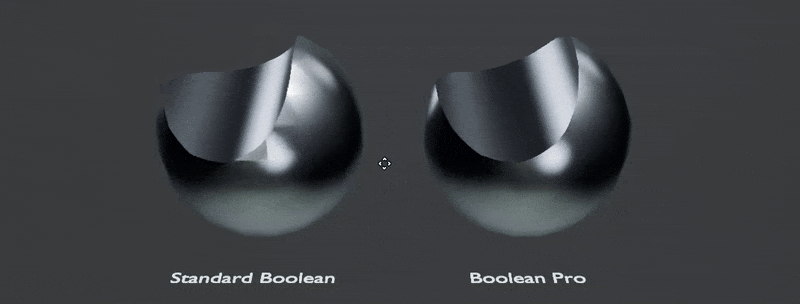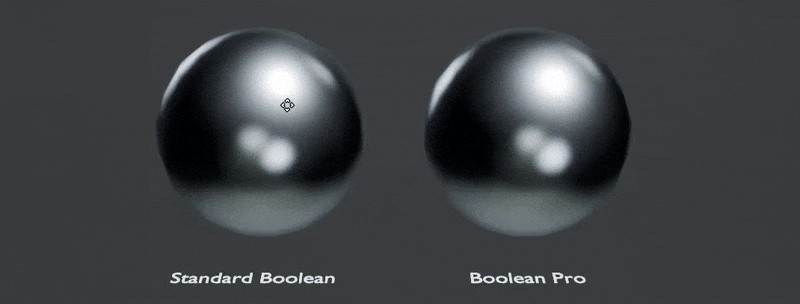
The most powerful feature is transferring the normals automatically from boolean inputs for perfect boolean normals:
The cutter object can be given an outset (expanded) with even thickness before cutting:
There is also a Slice operation with optional inset:
| Intersect | Union | Difference | Slice |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Options¶
Main¶
- Operation: Which boolean operation to perform.
- Intersect: Keep the part of the mesh that is shared between inputs.
- Union: Combine input meshes into a single mesh.
- Difference: (Default) Subtract input meshes from source mesh.
- Slice: Slice source mesh with input meshes. This combines "Intersect" and "Difference" into the same output.
- Object: Mesh object to use for boolean operation.
- Collection: Collection containing mesh objects to use for boolean operation.
- Solver:
- Float: Simple solver with good performance.
- Exact: Slower solver with best results on coplanar faces.
- Manifold: (Default) Fastest solver that only works on manifold meshes, but gives better results.
- Outset: Expands the cutter mesh with even thickness.
- Inset (Slice Mode): Offsets the cutter inwards for the intersect boolean to give a gap between meshes.
Weld¶
- Merge by Distance: Merge vertices based on distance.
- Distance: Distance at which to merge vertices.
Shading¶
- Materials: How to assign materials to new faces.
- Index Based: Match material index from boolean meshes.
- Specify: Specify a material to apply to all new faces.
- Transfer: Transfer materials from boolean meshes. This might not be accurate when using collections.
- Transfer Normals: Use normals from input meshes. Produces the best normals.
- Mark Sharp: Mark all intersection edges between meshes as sharp.
Solver Options¶
- Result: Whether to output a solid object or a cut surface.
- Solid: Output full Boolean result.
- Surface: Output a cut surface with open edges where new faces would appear.
- Sequential (Float solver only): Perform Booleans one mesh island at a time. This often gives better results but can be slower.
- Self Intersection (Exact solver only): Correctly calculates cases when one or both operands have self-intersections. This involves more calculations making the node slower.
- Hole Tolerant: Optimizes the Boolean output for non-manifold geometry at the cost of increased computational time. Because of the performance impact, this option should only be enabled when the solver demonstrates errors with non-manifold geometry.