Surface Project¶
Project and blend geometry onto other mesh surfaces. Transfer normals and UVs for a seamless blend.
Open Edges
This modifier works best on meshes with "open edges", i.e. non-solid objects. These edges are used as the base for most masking methods.
Examples¶
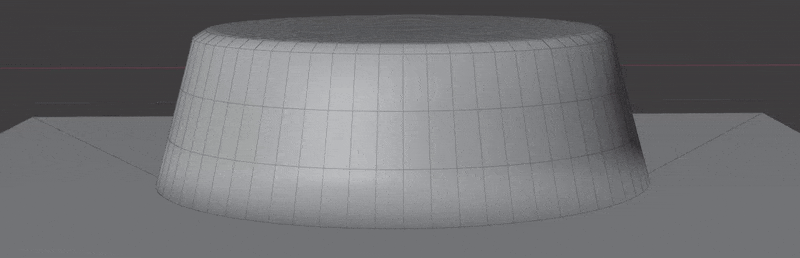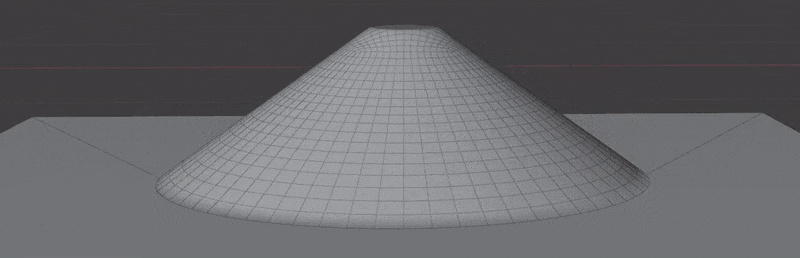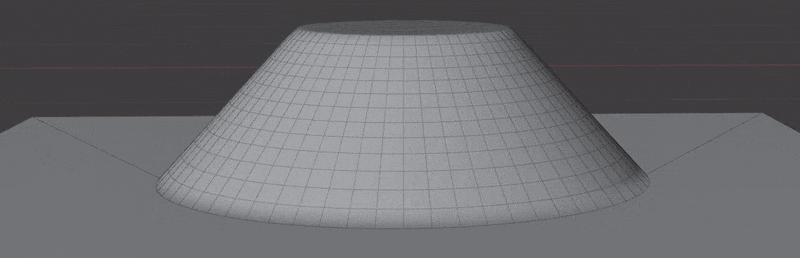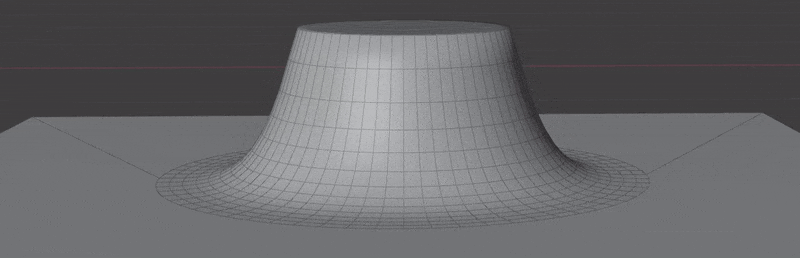
Examples can be found in the Surface Project/Insert scene in the example file.
Options¶
Projection Targets¶
Choose which meshes to project to.
- Target Objects: How many mesh objects to project to.
- Objects: Choose individual mesh objects to project to.
- Collection: Choose a collection containing mesh objects to project to.
Projection¶
Define how mesh is projected to surfaces.
- Method: Method for vertex projection:

- Wrap to Surface: Wrap mesh to target surface. Points will be projected to target surface and re-displaced based on their calculated height.
- Blend with Surface: Project points to target surface then blend between original and projected positions.
- Project Decal: Flatten geometry to target surface while keeping original normals. Ideal for "floaters" intended for baking.
- Surface Offset: Move projected vertices a fixed amount towards or away from the target surface.
Projection Direction¶
Control the direction and properties of surface projection.
- Project Direction: Define direction of projection rays:
- Object Direction: Direction in object space (default -Z).
- World Direction: Direction in world space (default -Z).
- Mesh Normal: Use individual point normals.
- Mesh Island Normal: Use the average normal of each mesh island.
- Mesh Tangent: Use individual point tangents.
- Surface Normal: Use the normal of the closest part of target surface.
- Base Height: How height is calculated for Wrap to Surface and Project Decal projection methods:
- Boundary Center: Calculate height from a plane defined by the center of the boundary and the projection direction.
- Object Origin: Calculate height from a plane defined by the objects origin and the projection direction.
- Re-Displace: When using Wrap to Surface. Direction to apply calculated height:
- Projection: Apply height displacement using the projection direction.
- Surface Normal: Apply height displacement using the normal of the target surface.
- Ray Length: Maximum distance rays will collide with target surface. Best to keep at a large enough value that all points collide.
- No Hit: Change behavior of vertices when projection rays miss:
- Unchanged: Do not move vertex.
- Closest Surface to Max Dist: Move vertex to the maximum distance in ray direction then snap to closest point on target surface.
Projection Masking¶
Control how projection is masked. See Mask Falloff.
- Vertex Group: Choose a vertex group to project.
Transfer Normals¶
Transfer normals from target surfaces. Internally this uses Normal Transfer. Normals are transferred after vertex projection, using the closest target surface.
- Normal Domain: Whether normals are stored on points (smooth) or face corners (allows sharp edges).
- Normal Masking: How to mask the normal transfer:
- Projection Mask: Use the same mask used for vertex projection.
- New Mask: Create a new mask using mask falloff.
- Vertex Group: Limit all normal transfer to a vertex group.
Transfer UVs¶
Transfer UVs from target surface.
- UV Map From: Which UV Map to transfer from the surface.
- UV Map To: Which UV Map to write to on this object.